FROM POWDER TO PERFORMANCE
HANA Advanced Material Technology
FROM POWDER TO PERFORMANCE
HANA Advanced Material Technology

Additive manufacturing is a new technology to manufacture precise components(parts) by adding successive layers using powders, based on computer-aided design(CAD) models.
AM is receiving great attention nowadays. It doesn’t need processing compared to the manufacture of metal which needs casting and processing. No restriction on design and few material loss make AM more special. AM considered making high quality and customized components used in aerospace, military, automobiles, and biology.
To make excellent products using additive manufacturing technology, high-quality metal powders,
which need high density, high flowability, low oxygen concentration are required.

PBF is an AM technology which spread metal powders on the selective parts using
a printed energy source, add powders by layer-by-layer, manufacture customized and precise components. A selective laser melting technology, one of the typical PBF technologies, is using a laser as an energy source. The layer thickness ranged as narrow as 20~100μm. Metal powders should be ranged 10~50μm and spherical for highflowability.
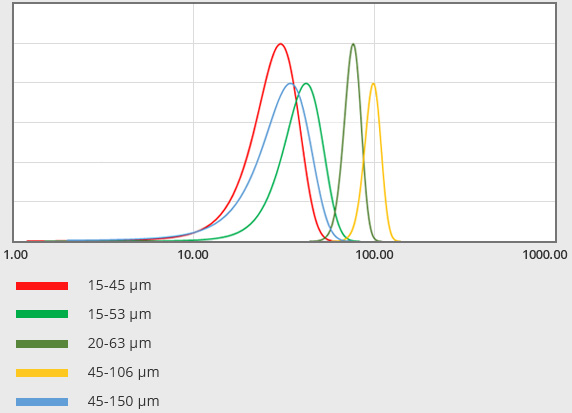
Direct energy deposition is an AM technology which supplies metal powders and heat source at the same time, different from powder bed fusion technology. The layer thickness ranged 0.2~0.8mm, relatively movable powders are used, compared to powders for PBF.
Fused deposition modeling (fused filament fabrication) is an AM technology which manufactures components by the process of extrusion of filaments that made of metal powders and binder, controlling shape, debinding through degreasing, sintering in high temperature. Fine powders less than 20 μm are preferred to develop packing fraction for the powders used in FDM technology.